Understanding Liver Cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic liver condition characterized by progressive replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, leading to impaired liver function. This condition represents the advanced stage of various chronic liver diseases.
Common Symptoms
Compensated Stage:
-
Mild abdominal discomfort
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Reduced appetite
-
Digestive issues
-
Often asymptomatic
Decompensated Stage:
-
Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
-
Abdominal swelling (ascites)
-
Easy bruising and bleeding
-
Mental confusion
-
Swollen legs
Disease Classification
By Disease Progression:
-
Compensated cirrhosis: Liver functions adequately despite damage
-
Decompensated cirrhosis: Liver function significantly impaired
By Nodule Characteristics:
-
Micronodular cirrhosis (small, uniform nodules)
-
Macronodular cirrhosis (larger, varied nodules)
-
Mixed nodular cirrhosis
Primary Contributing Factors
Common Causes:
-
Chronic viral hepatitis (HBV, HCV)
-
Alcohol-related liver disease
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
Autoimmune conditions
-
Genetic and metabolic disorders
Risk Factors:
-
Chronic alcohol consumption
-
Viral hepatitis infections
-
Obesity and metabolic syndrome
-
Certain medications
-
Genetic predisposition
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers may recommend:
-
Physical examination
-
Blood tests (liver function tests)
-
Imaging studies (ultrasound, CT, MRI)
-
Specialized liver assessments
-
Endoscopic evaluation
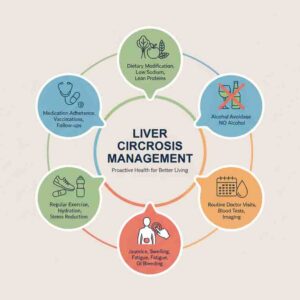
Management Considerations
Lifestyle Adjustments:
-
Dietary modifications
-
Alcohol avoidance
-
Regular monitoring
-
Healthy weight maintenance
Medical Supervision:
-
Regular follow-up visits
-
Complication monitoring
-
Specialist consultations
-
Individualized care plans
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare professional if experiencing:
-
Persistent abdominal discomfort
-
Unexplained fatigue
-
Yellowing of skin or eyes
-
Abdominal swelling
-
Changes in mental alertness
Medical Disclaimer: This information provides educational content about liver cirrhosis. Individual medical conditions vary significantly, and this content should not replace professional healthcare advice. Always consult qualified medical professionals for proper diagnosis and personalized management recommendations.