Clinical Definition
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a common systemic viral infection characterized by vesicular exanthema on the palms, soles, and buttocks, accompanied by oral enanthem (ulcerative stomatitis). It is predominantly caused by the Enterovirus genus, specifically Coxsackievirus A16 (CV-A16) and Enterovirus 71 (EV-A71). While typically self-limiting, EV-A71 infections are notably associated with severe neurological complications, including brainstem encephalitis and neurogenic pulmonary edema.
Clinical Coding & Classification
| System / Category | Code(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | B08.4 | Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis with exanthem |
| ICD-10-CM | A87.0 | Enteroviral meningitis (Complication) |
| CPT (Lab) | 87498 | Infectious agent detection by nucleic acid (DNA/RNA); Enterovirus |
| Affected System | Integumentary; Neurological | Viral Exanthem |
Epidemiology & Statistics
HFMD primarily affects infants and children younger than 5 years, though adult cases occur. Outbreaks are cyclical, peaking in summer and early autumn in temperate climates, while circulating year-round in tropical regions. Transmission is highly efficient via the fecal-oral route or respiratory droplets, leading to rapid spread in daycare and school settings.
Pathophysiology (Mechanism)
The pathogenesis follows a distinct viral replication pathway:
1. Portal of Entry: Virus enters via the oropharynx or intestinal tract.
2. Primary Replication: Occurs in the lymphoid tissues of the pharynx (tonsils) and the gut (Peyer’s patches).
3. Viremia: Minor viremia disseminates the virus to the reticuloendothelial system, followed by major viremia spreading to skin, mucous membranes, and (in severe strains like EV-71) the Central Nervous System (CNS).
4. Cytopathic Effect: Viral replication in keratinocytes leads to vesicle formation and cell lysis.
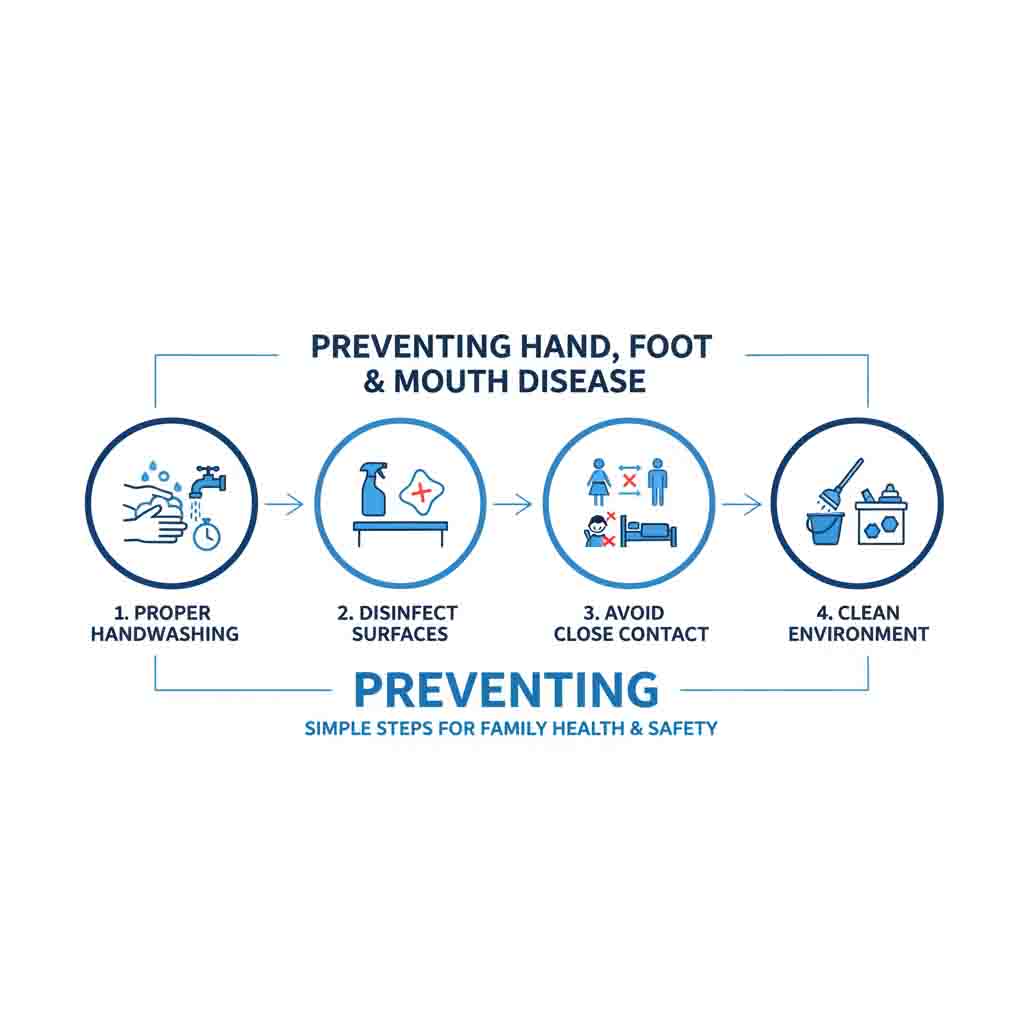
Standard Management Protocols
Management is primarily supportive, with a focus on hydration and pain control.
- Supportive Care:
- Oral Hydration: Critical to prevent dehydration due to odynophagia (painful swallowing).
- Analgesics/Antipyretics: (e.g., Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen) Systemic pain relief.
- Topical Agents: (e.g., “Magic Mouthwash” formulations containing lidocaine/diphenhydramine) Used for symptomatic relief of stomatitis.
- Advanced Intervention (Severe EV-71):
- IVIG (Intravenous Immunoglobulin): May be considered in cases with severe CNS involvement (encephalitis) to neutralize viral load and modulate inflammation.
Healthcare Resource Utilization
While most cases are managed outpatient, resource utilization spikes during outbreaks due to:
- Pediatric ER Visits: High volume of presentations for dehydration requiring IV fluids.
- Isolation Protocols: Strict contact precautions required in hospital settings to prevent nosocomial transmission.