Procedure Overview & Indications
An appendectomy is the surgical resection of the vermiform appendix. It is the standard-of-care treatment for acute appendicitis, a condition involving inflammation and infection of the appendix. The primary indication is to remove the inflamed organ before it ruptures, which can lead to peritonitis and sepsis. Other, less common indications include the removal of an appendiceal tumor (carcinoid or adenocarcinoma) or prophylactic removal during other abdominal surgeries.
Procedural Coding
CPT Code Range: 44950 – 44979
- 44970: Laparoscopy, surgical, appendectomy
- 44950: Appendectomy (Open approach)
ICD-10-PCS: 0DTJ0ZZ (Resection of Appendix, Open Approach), 0DTJ4ZZ (Resection of Appendix, Percutaneous Endoscopic Approach)
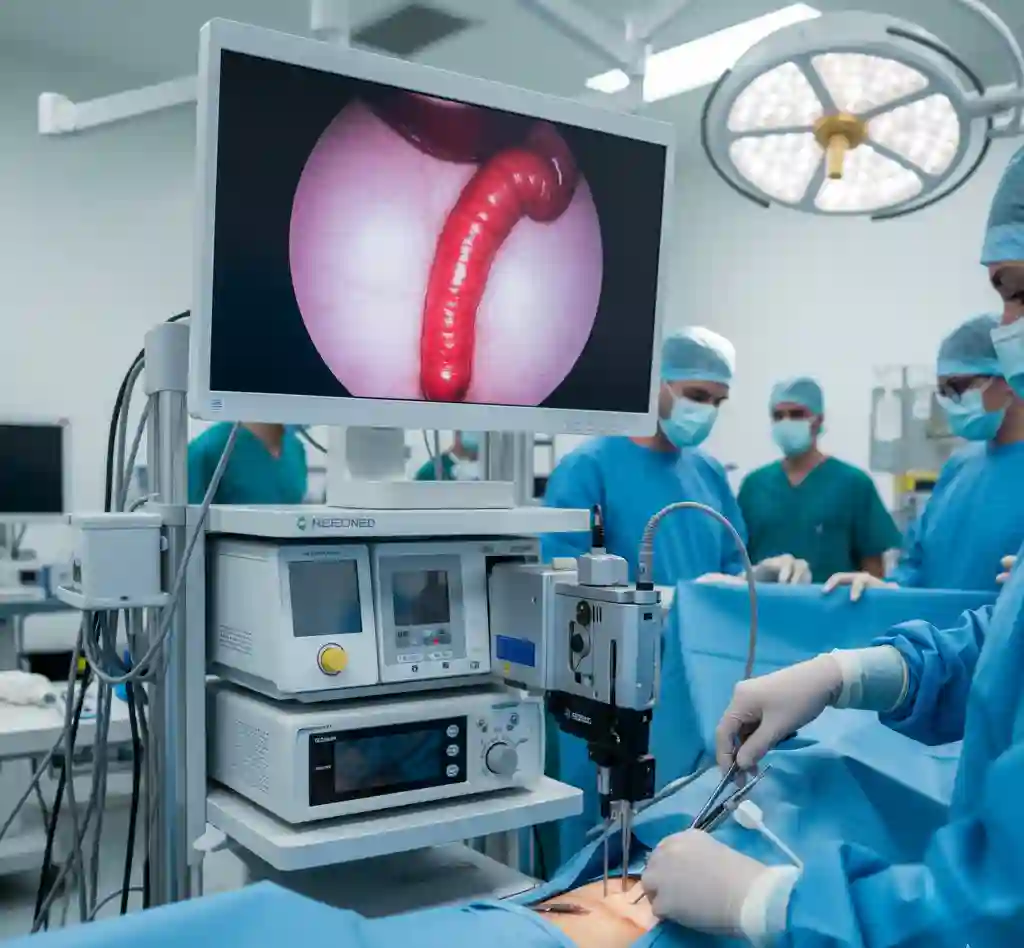
Technology & Equipment
The equipment utilized depends on the surgical approach (laparoscopic vs. open). The laparoscopic approach is more common and involves a laparoscopic tower, which includes a high-definition monitor, a camera unit, a xenon light source, and a CO2 insufflator to create a pneumoperitoneum. Essential instrumentation includes:
- Trocars (typically 5mm and 10-12mm) for surgical access.
- A high-definition laparoscope (camera).
- Laparoscopic graspers and dissectors.
- An energy device for vessel sealing and dissection (e.g., an electrosurgical or ultrasonic device).
- A laparoscopic stapler or endoscopic loop ligatures for division of the appendiceal base.
- A specimen retrieval bag.
An open procedure utilizes a standard major instrument tray with scalpels, forceps, retractors (e.g., Richardson retractors), and suture materials.
Methodology (Step-by-Step Summary)
- Preparation Phase: The patient is placed under general anesthesia in a supine position. The abdomen is prepped with an antiseptic solution and draped in a sterile fashion. Prophylactic antibiotics are administered.
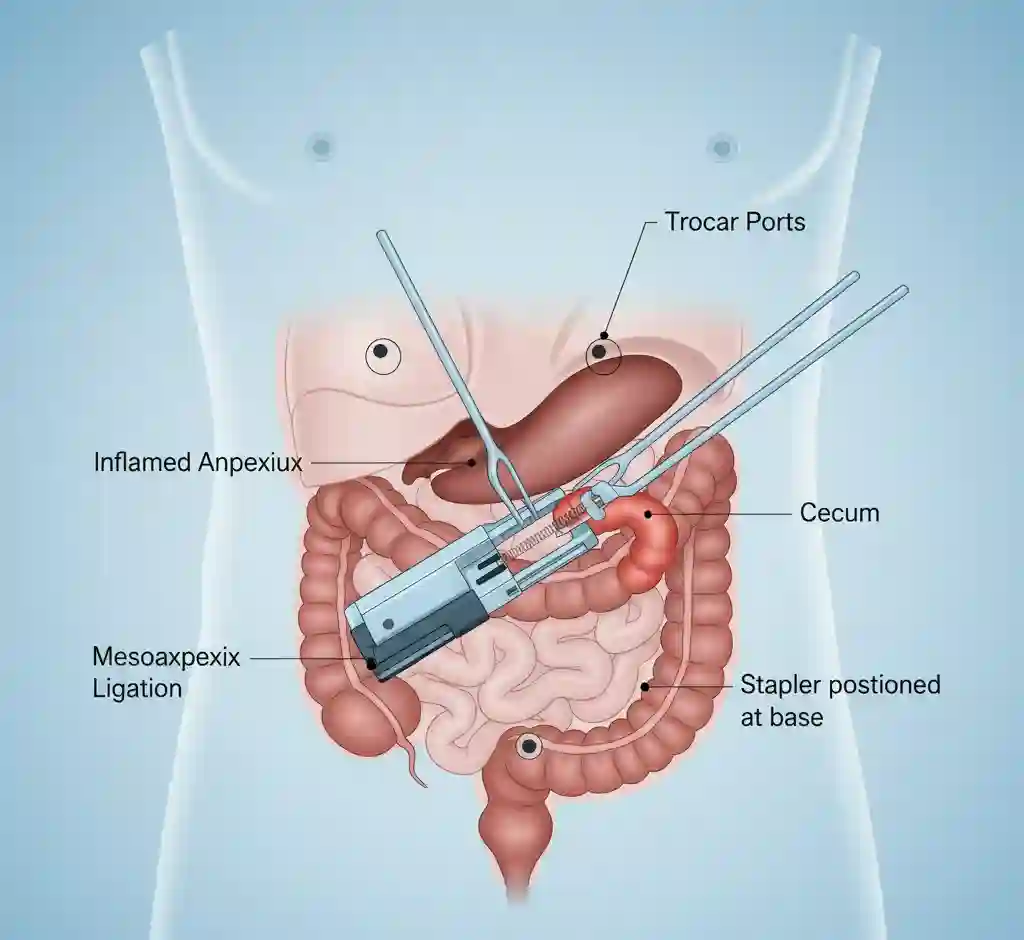
- Procedural Phase (Laparoscopic):
- An initial incision is made, typically near the umbilicus, and pneumoperitoneum is established using CO2 gas.
- Trocars are inserted through small incisions to provide access for the laparoscope and instruments.
- The appendix is identified and mobilized. The mesoappendix, which contains the appendiceal artery, is dissected and ligated using an energy device or clips.
- The base of the appendix is divided using a surgical stapler or ligated with sutures.
- The resected appendix is placed into a retrieval bag and removed through one of the trocar sites to prevent wound contamination.
- The surgical field is inspected for hemostasis, and the pneumoperitoneum is released.
- Post-Procedural Monitoring: The patient is transferred to the Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) for monitoring of vital signs and pain control. They are typically advanced to a clear liquid diet once bowel function returns and are often discharged within 24-48 hours.
Clinical Significance & Outcomes
A successful appendectomy results in the complete resolution of the infection and inflammation associated with appendicitis. The procedure has a very high success rate, exceeding 95% for uncomplicated cases. Laparoscopic appendectomy, in particular, is associated with favorable outcomes, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and a faster return to normal activities compared to the open approach. The primary outcome is the prevention of perforation and subsequent peritonitis. The resected specimen is sent for histopathological analysis to confirm the diagnosis and rule out malignancy.