Pharmacological Classification
Class: HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor (Statin); Lipid-modifying agent.
ATC Code: C10AA05 (Cardiovascular system > Lipid modifying agents > Lipid modifying agents, plain > HMG CoA reductase inhibitors).
Common Trade Names: Lipitor (Reference only; regional trade names vary).
Mechanism of Action (MOA)
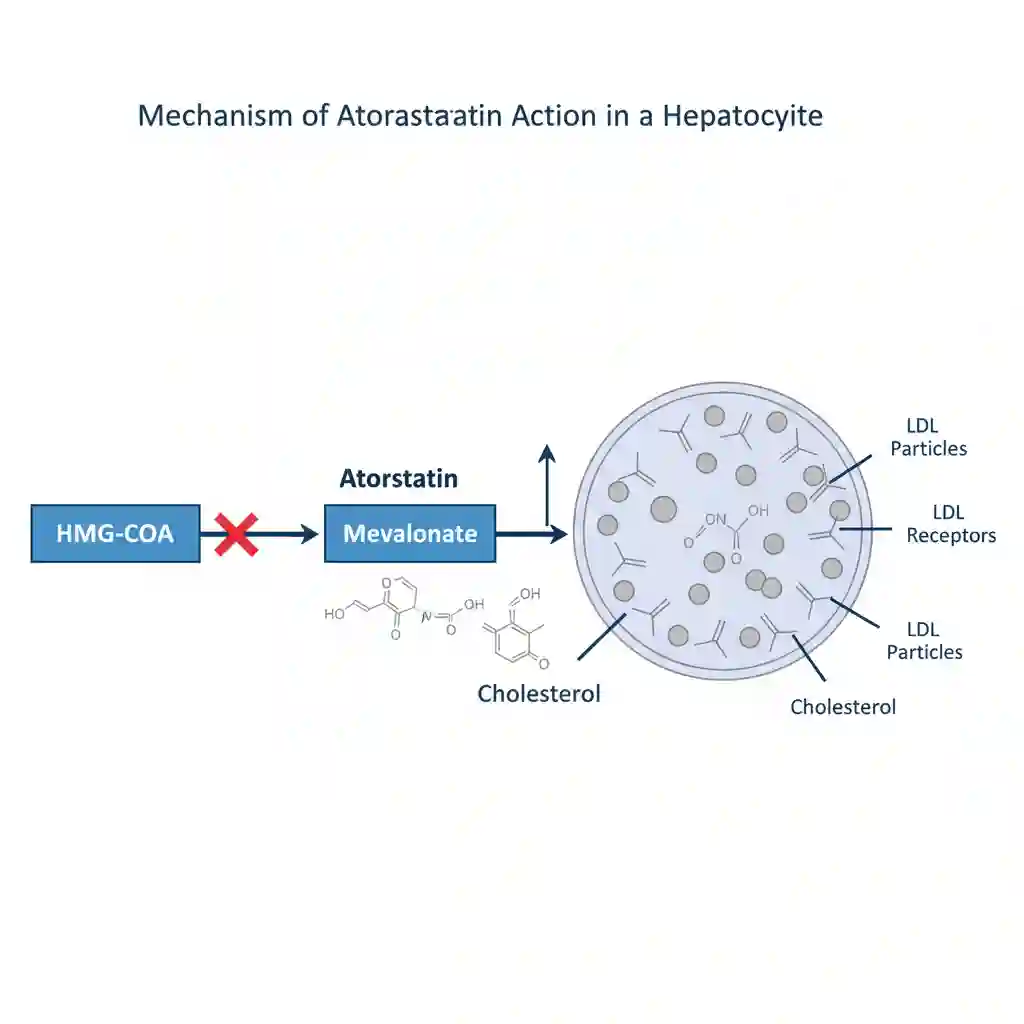
Atorvastatin is a selective, competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A to mevalonate—a precursor of sterols, including cholesterol. The primary site of action is the hepatocyte (liver cell).
The physiological reduction in hepatic cholesterol synthesis triggers a compensatory upregulation of LDL receptors (LDLR) on the hepatocyte cell surface. This upregulation enhances the catabolism and clearance of LDL-cholesterol from the systemic circulation. Additionally, Atorvastatin demonstrates pleiotropic effects, including improvement of endothelial function, stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques, and inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.
Pharmacokinetics (PK Profile)
- Absorption: Rapidly absorbed after oral administration; maximum plasma concentrations (Tmax) occur within 1 to 2 hours. However, the absolute bioavailability is approximately 14% due to extensive presystemic clearance in the gastrointestinal mucosa and liver.
- Distribution: Highly protein-bound in plasma (≥98%), primarily to albumin. The mean volume of distribution (Vd) is approximately 381 L.
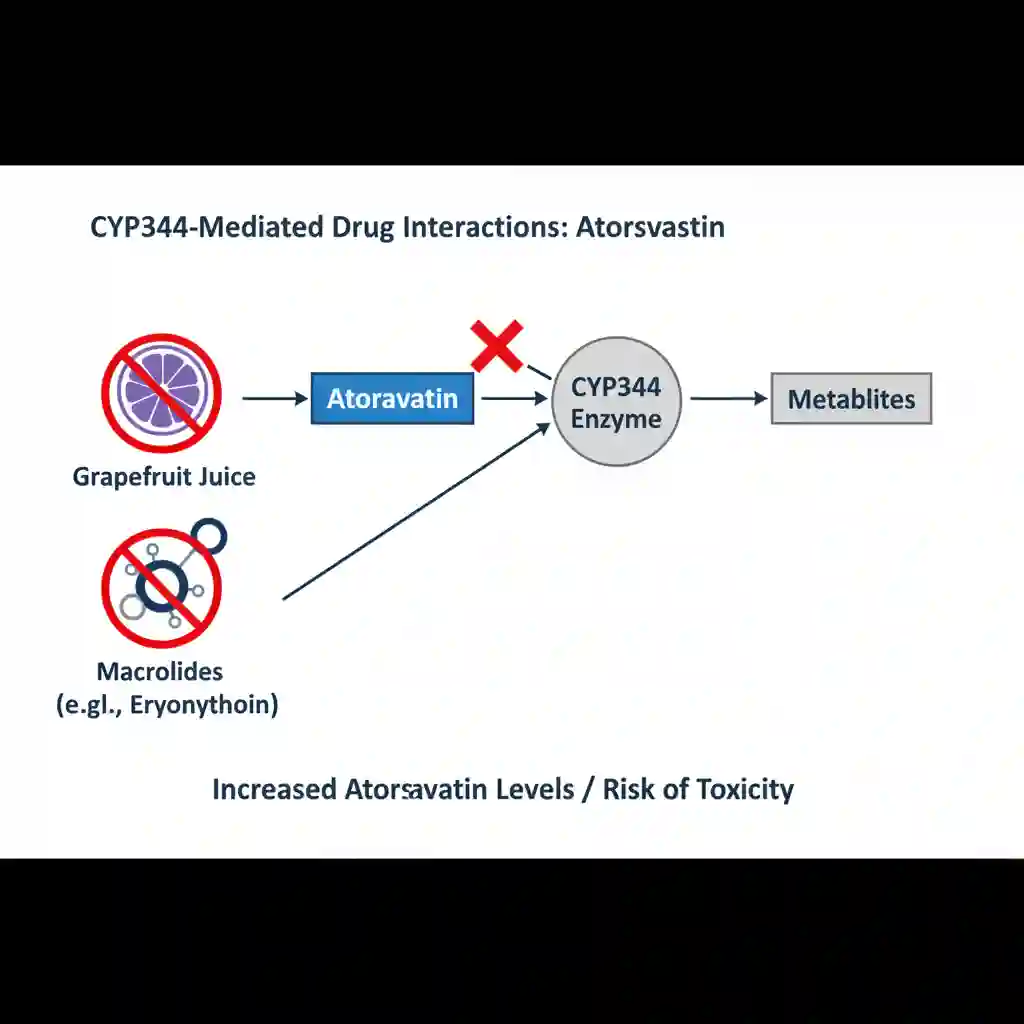
- Metabolism: Extensively metabolized by the hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 to form ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives. Notably, approximately 70% of circulating inhibitory activity for HMG-CoA reductase is attributed to these active metabolites.
- Excretion: Primarily eliminated in bile following hepatic and/or extrahepatic metabolism. It does not undergo significant enterohepatic recirculation. The plasma elimination half-life is approximately 14 hours; however, the half-life of inhibitory activity is 20–30 hours due to the contribution of active metabolites.
Clinical Indications (FDA Labeling)
Atorvastatin is indicated as an adjunct to diet in the management of lipid disorders and cardiovascular risk reduction:
- Hyperlipidemia: To reduce elevated Total-C, LDL-C, ApoB, and TG levels and to increase HDL-C in patients with primary hyperlipidemia (heterozygous familial and nonfamilial) and mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb).
- Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH): To reduce Total-C and LDL-C.
- Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: Indicated to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and revascularization procedures in patients with risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD).
Contraindications & Safety Warnings
Regulatory safety protocols highlight hepatic and musculoskeletal risks:
- Active Liver Disease: Contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases (ALT/AST).
- Skeletal Muscle Effects: Risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of muscle tissue leading to renal failure). The risk is increased by concurrent administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine, clarithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors).
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Category X. Cholesterol biosynthesis is essential for fetal development; atorvastatin is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant.