Clinical Definition
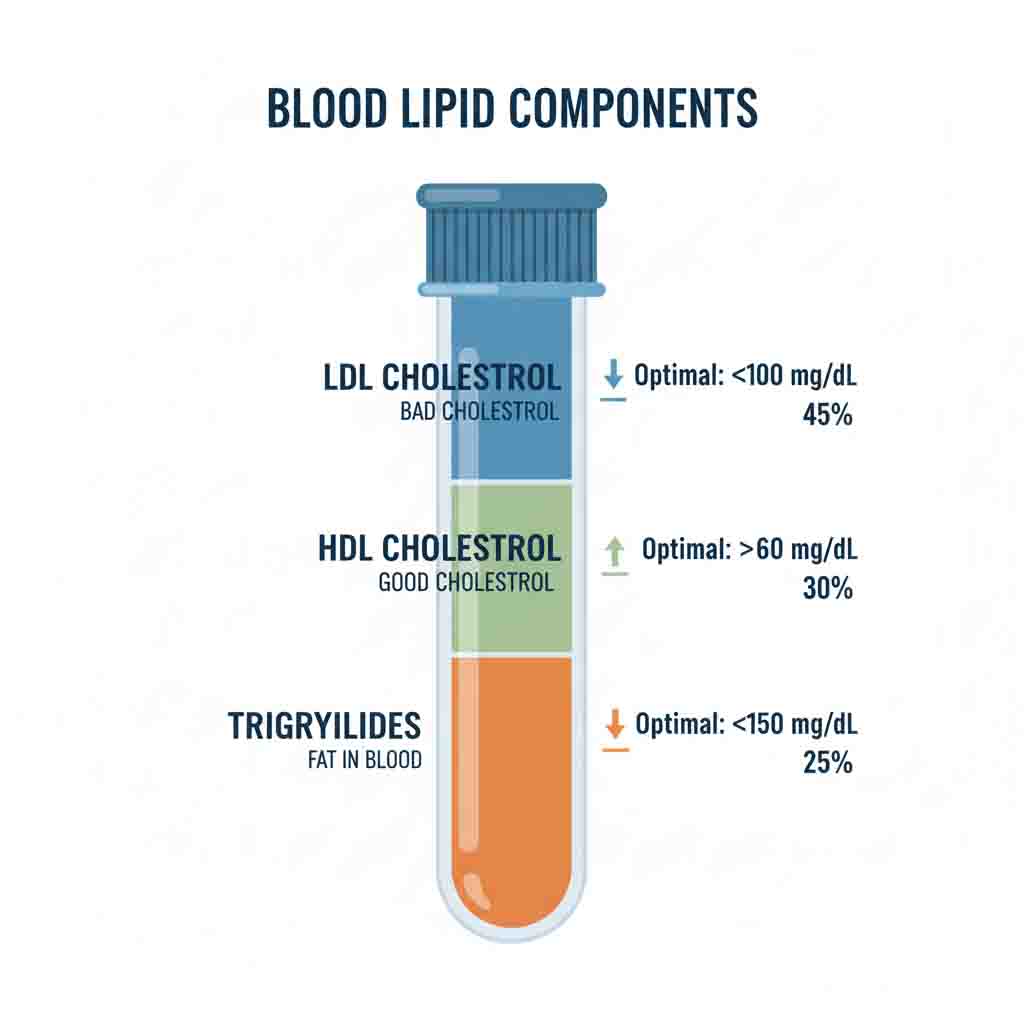
Hyperlipidemia, clinically encompassing Dyslipidemia, refers to aberrant levels of plasma lipoproteins, including elevated Total Cholesterol (TC), Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C), and Triglycerides (TG), or decreased High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C). It is a primary modifiable risk factor for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). Etiologically, it is classified into Primary (familial/genetic, e.g., Familial Hypercholesterolemia) and Secondary (acquired via lifestyle, diabetes, or hypothyroidism) forms.
Clinical Coding & Classification
| System / Category | Code(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | E78.00 | Pure hypercholesterolemia, unspecified (includes Familial Hypercholesterolemia) |
| ICD-10-CM | E78.1 | Pure hyperglyceridemia (High Triglycerides) |
| ICD-10-CM | E78.2 | Mixed hyperlipidemia |
| CPT (Lab) | 80061 | Lipid panel (Total, HDL, Triglycerides) |
| CPT (Therapeutic) | 36516 | Therapeutic apheresis; for selective removal of LDL (LDL Apheresis) |
Epidemiology & Statistics
Dyslipidemia is highly prevalent, affecting approximately 38% of adults in the United States. It is a cornerstone of Metabolic Syndrome. Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH), a genetic form associated with premature coronary artery disease, has a heterozygous prevalence of approximately 1 in 250 individuals, yet remains significantly underdiagnosed.
Pathophysiology (Mechanism)
Lipid metabolism involves the transport of hydrophobic lipids via hydrophilic lipoproteins:
1. Exogenous Pathway: Dietary fats are absorbed and transported as chylomicrons.
2. Endogenous Pathway: The liver secretes VLDL, which is hydrolyzed to IDL and then LDL. LDL transports cholesterol to peripheral tissues.
3. LDL Receptor Pathway: The liver clears circulating LDL via LDL receptors (LDLR). Defects in LDLR function (or degradation by PCSK9) lead to elevated serum LDL-C.
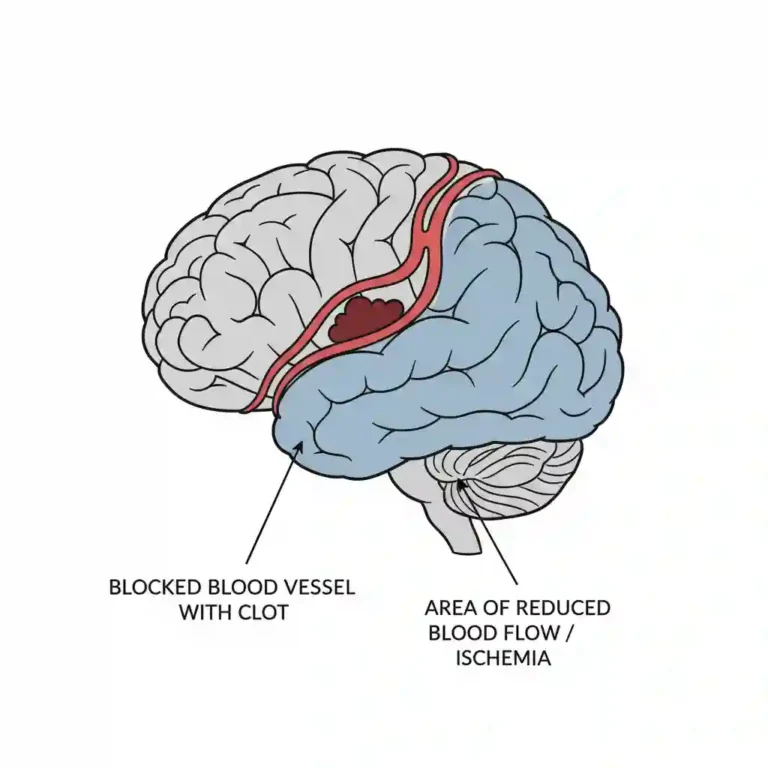
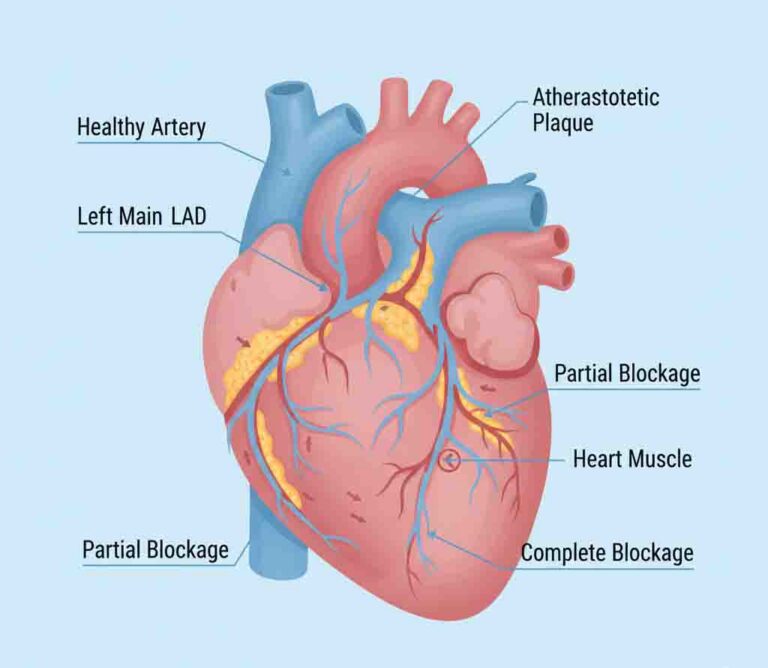
4. Atherogenesis: Excess LDL particles penetrate the arterial endothelium, undergo oxidation, and are engulfed by macrophages to form foam cells—the hallmark of the atherosclerotic plaque.
Standard Management Protocols
Therapy is guided by ASCVD risk stratification (e.g., ACC/AHA Risk Calculator) and LDL-C reduction targets.
- Pharmacological Classes:
- HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins): (e.g., Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin) First-line therapy. Inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis and upregulate hepatic LDL receptors. High-intensity regimens reduce LDL-C by ≥50%.
- Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors: (e.g., Ezetimibe) Inhibits Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1) protein at the brush border.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: (e.g., Evolocumab, Alirocumab) Monoclonal antibodies that prevent PCSK9-mediated degradation of LDL receptors. Indicated for FH or clinical ASCVD requiring additional lowering.
- Fibrates / Omega-3 Fatty Acids: (e.g., Fenofibrate, Icosapent Ethyl) Primarily used for severe hypertriglyceridemia (>500 mg/dL) to prevent pancreatitis.
Healthcare Resource Utilization
Hyperlipidemia management involves lifelong surveillance and intervention to prevent high-cost events:
- Preventive Cardiology: Routine lipid panels and ASCVD risk assessments.
- Acute Events: Uncontrolled dyslipidemia leads to Myocardial Infarction and Stroke, driving emergency and inpatient costs.